redis数据结构-跳跃表
温馨提示:
本文最后更新于 2023年02月03日,已超过 937 天没有更新。若文章内的图片失效(无法正常加载),请留言反馈或直接联系我。
跳跃表
redis的有序集合,使用的是hash字典+跳跃表实现的
typedef struct zskiplist {
struct zskiplistNode *header, *tail;
unsigned long length;
int level;
} zskiplist;
typedef struct zset {
dict *dict;
zskiplist *zsl;
} zset;
跳跃表基本结构
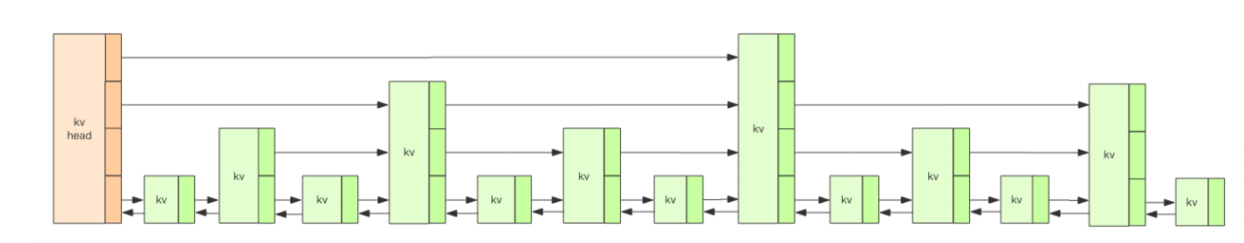
跳跃表结构分为N层,数据量从上到下,redis的跳跃表总共有64层,最多可以容纳2^64个元素,每个kv块对应的是zskiplistNode 结构.
typedef struct zskiplistNode {
sds ele;
double score;
struct zskiplistNode *backward;
struct zskiplistLevel {
struct zskiplistNode *forward;
unsigned long span;
} level[];
} zskiplistNode;
kvheade 的value值为空,score为0,每次查找时,从head的最顶层开始查找,通过score范围查找,再进行降级:
x = zsl->header;//从header开始查找
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {//从最顶层开始查找
while (x->level[i].forward &&//判断是否存在小于当前分数的元素
(x->level[i].forward->score < curscore ||//比较分数是否小于
(x->level[i].forward->score == curscore &&//当分数相同时
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0)))//比较key字符
{
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
update[i] = x;
}
当分数一样时,需要根据sdscmp函数判断key,根据key的长度,字符来判断大小:
/* Compare two sds strings s1 and s2 with memcmp().
*
* Return value:
*
* positive if s1 > s2.
* negative if s1 < s2.
* 0 if s1 and s2 are exactly the same binary string.
*
* If two strings share exactly the same prefix, but one of the two has
* additional characters, the longer string is considered to be greater than
* the smaller one. */
int sdscmp(const sds s1, const sds s2) {
size_t l1, l2, minlen;
int cmp;
l1 = sdslen(s1);
l2 = sdslen(s2);
minlen = (l1 < l2) ? l1 : l2;
cmp = memcmp(s1,s2,minlen);
if (cmp == 0) return l1>l2? 1: (l1<l2? -1: 0);
return cmp;
}
插入逻辑
对于每个新插入的节点,都默认为第1层,同时有一定概率升级层数.
int zslRandomLevel(void) {
int level = 1;
while ((random()&0xFFFF) < (ZSKIPLIST_P * 0xFFFF))
level += 1;
return (level<ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL) ? level : ZSKIPLIST_MAXLEVEL;
}
可以看到,在redis中,概率为ZSKIPLIST_P,默认为25%几率升级
在插入前,需要先获取到每一层小于该分数的第一个字值,定位出来,因为需要更新前置元素,同时还要获取排名进行更新
x = zsl->header;
for (i = zsl->level-1; i >= 0; i--) {
/* store rank that is crossed to reach the insert position */
rank[i] = i == (zsl->level-1) ? 0 : rank[i+1];
while (x->level[i].forward &&
(x->level[i].forward->score < score ||
(x->level[i].forward->score == score &&
sdscmp(x->level[i].forward->ele,ele) < 0)))
{
rank[i] += x->level[i].span;
x = x->level[i].forward;
}
update[i] = x;
}
如果随机的层数大于当前层数,则需要创建一个新的层
level = zslRandomLevel();
if (level > zsl->level) {
for (i = zsl->level; i < level; i++) {
rank[i] = 0;
update[i] = zsl->header;
update[i]->level[i].span = zsl->length;
}
zsl->level = level;
}
然后就是创建一个zskiplistNode结构体,进行插入
x = zslCreateNode(level,score,ele);
for (i = 0; i < level; i++) {
x->level[i].forward = update[i]->level[i].forward;
update[i]->level[i].forward = x;
/* update span covered by update[i] as x is inserted here */
x->level[i].span = update[i]->level[i].span - (rank[0] - rank[i]);
update[i]->level[i].span = (rank[0] - rank[i]) + 1;
}
/* increment span for untouched levels */
for (i = level; i < zsl->level; i++) {
update[i]->level[i].span++;
}
x->backward = (update[0] == zsl->header) ? NULL : update[0];
if (x->level[0].forward)
x->level[0].forward->backward = x;
else
zsl->tail = x;
zsl->length++;
return x;
正文到此结束
- 本文标签: 编程语言 数据库
- 本文链接: https://www.php20.cn/article/410
- 版权声明: 本文由仙士可原创发布,转载请遵循《署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)》许可协议授权