linux定时任务
linux定时任务在一般情况下是默认启动的,通过crontab命令去控制
crontab默认配置文件
一般情况下,定时任务的配置文件,都在/etc/crontab文件中:
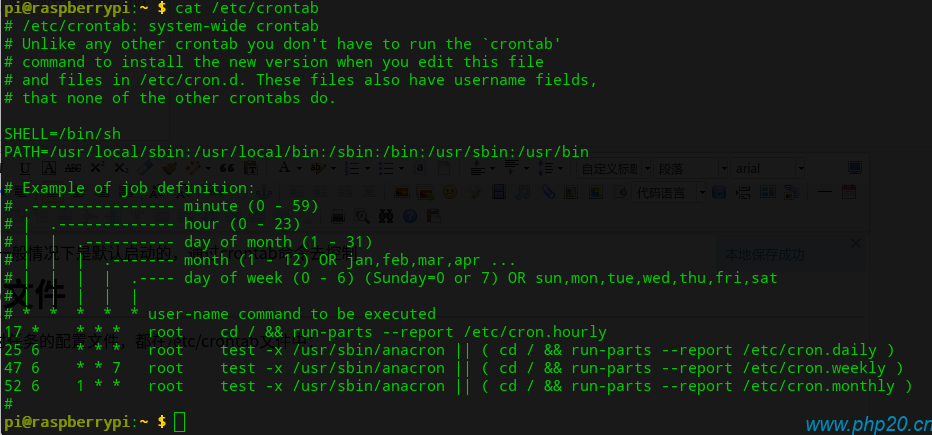
图为某系统默认的定时任务,可看出,根据不同的任务规则,执行了不同的任务,里面的配置大概分为以下几种:
cat /etc/crontab
SHELL=/bin/bash # 第一行SHELL变量指定了系统要使用哪个shell,这里是bash,
PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin # 第二行PATH变量指定了系统执行 命令的路径
MAILTO=root # 第三行MAILTO变量指定了crond的任务执行信息将通过电子邮件发送给root用户,,如果MAILTO变量的值为空,则表示不发送任务 执行信息给用户
MAILTO=HOME=/ # 第四行的HOME变量指定了在执行命令或者脚本时使用的主目录
# run-parts # 以下的都是设定的自动执行任务的条件和执行哪项任务
17 * * * * root cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.hourly
25 6 * * * root test -x /usr/sbin/anacron || ( cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.daily )
47 6 * * 7 root test -x /usr/sbin/anacron || ( cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.weekly )
52 6 1 * * root test -x /usr/sbin/anacron || ( cd / && run-parts --report /etc/cron.monthly )
用户定时任务配置
用户自定义的定时任务,将保存在/var/spool/cron/crontabs/文件夹中,文件根据用户名进行命名:
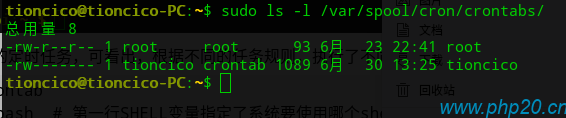
可直接编辑里面的文件,进行自定义定时任务,也可以通过crontab -e 命令编辑,下面将讲到
用户使用权限
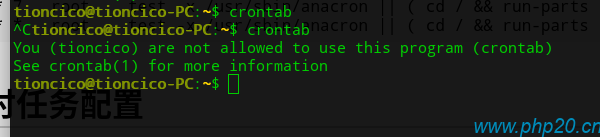
crontab中,可以通过/etc/cron.allow和/etc/cron.deny文件进行控制用户使用权限,规则如下:
cron.allow:定义允许使用crontab命令的用户
cron.deny:定义拒绝使用crontab命令的用户
1:如果存在allow文件,则检测该文件是否存在当前用户,不存在则提示没有权限
2:如果不存在allow,则检测deny,如果该文件存在当前用户,则提示没有权限
例如:
只允许root权限执行:
echo “” > /etc/cron.allow
直接写入空文件,则只能root执行crontab:
例如,允许tioncico,www用户执行
echo -e "tioncico\nwww" >/etc/cron.allow
例如,除了tioncico,其他用户都能执行:
echo -e "tioncico" >/etc/cron.deny
rm -rf /etc/cron.allow //删除白名单
crontab 命令
crontab -u 指定crontab的用户,如果不使用该参数,则默认为当前用户
crontab -l 输出用户的 crontab文件配置
crontab -e 编辑用户的定时任务文件
crontab -r 删除用户的文件
例如:
tioncico@tioncico-PC:~$ sudo crontab -u root -l
*/1 * * * * /usr/bin/curl http://dnf.php20.cn/ >/tmp/1.txt
*/1 * * * * echo 666 >/tmp/1.txt
tioncico@tioncico-PC:~$ sudo crontab -u tioncico -l
# Edit this file to introduce tasks to be run by cron.
#
# Each task to run has to be defined through a single line
# 省略内容
tioncico@tioncico-PC:~$ sudo crontab -e
tioncico@tioncico-PC:~$ sudo crontab -utioncico -r
tioncico@tioncico-PC:~$ sudo crontab -utioncico -l
no crontab for tioncico
tioncico@tioncico-PC:~$
crontab定时任务规则
从刚刚的那些内容我们可以看到,定时任务的前面是5段内容,用空格分开,后面是执行的命令,现在我们讲一讲这5段内容代表的意义
这5段内容分别代表了“分,时,日,月,周” 5种规则,例如:
* * * * * myCommand
星号代表了全部匹配,代表不管每周的周几,每年的几月,每月的几号,每天的几时,每时的每分钟,都会执行这个脚本
同样,除了星号,还有其他符号,符号如下:
crontab规则符号
* 代表着完全匹配 例如
* * * * * myCommand
/ number 代表每隔几次
*/2 * * * * myCommand 每两分钟执行
number 代表着准确的时间段
2 * * * * myCommand 每个小时的第2分钟执行
number,number, 代表着多个时间
2,5,8 * * * * myCommand 每个小时的第2分钟,第5分钟,第8分钟都执行
number-number 代表着一个时间段
2-37 * * * * myCommand 每个小时的2-37分钟都执行
需要注意的是,第五种规则,也就是周的时候,取值范围是0-6,匹配 周日-周六
crontab规则实例:
1 3-10 1,2 5 * myCommand 每年的5月1日,5月2日的3点-10点01分钟时执行
*/2 * * * 0 myCommand 每周日每隔2分钟执行一次
1 3 * * * myCommand 每天3点01分执行
* */1 * * * myCommand 每小时执行一次
* * * */1 * myCommand 每月执行一次
- 本文标签: 操作系统
- 本文链接: https://www.php20.cn/article/200
- 版权声明: 本文由仙士可原创发布,转载请遵循《署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际 (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)》许可协议授权